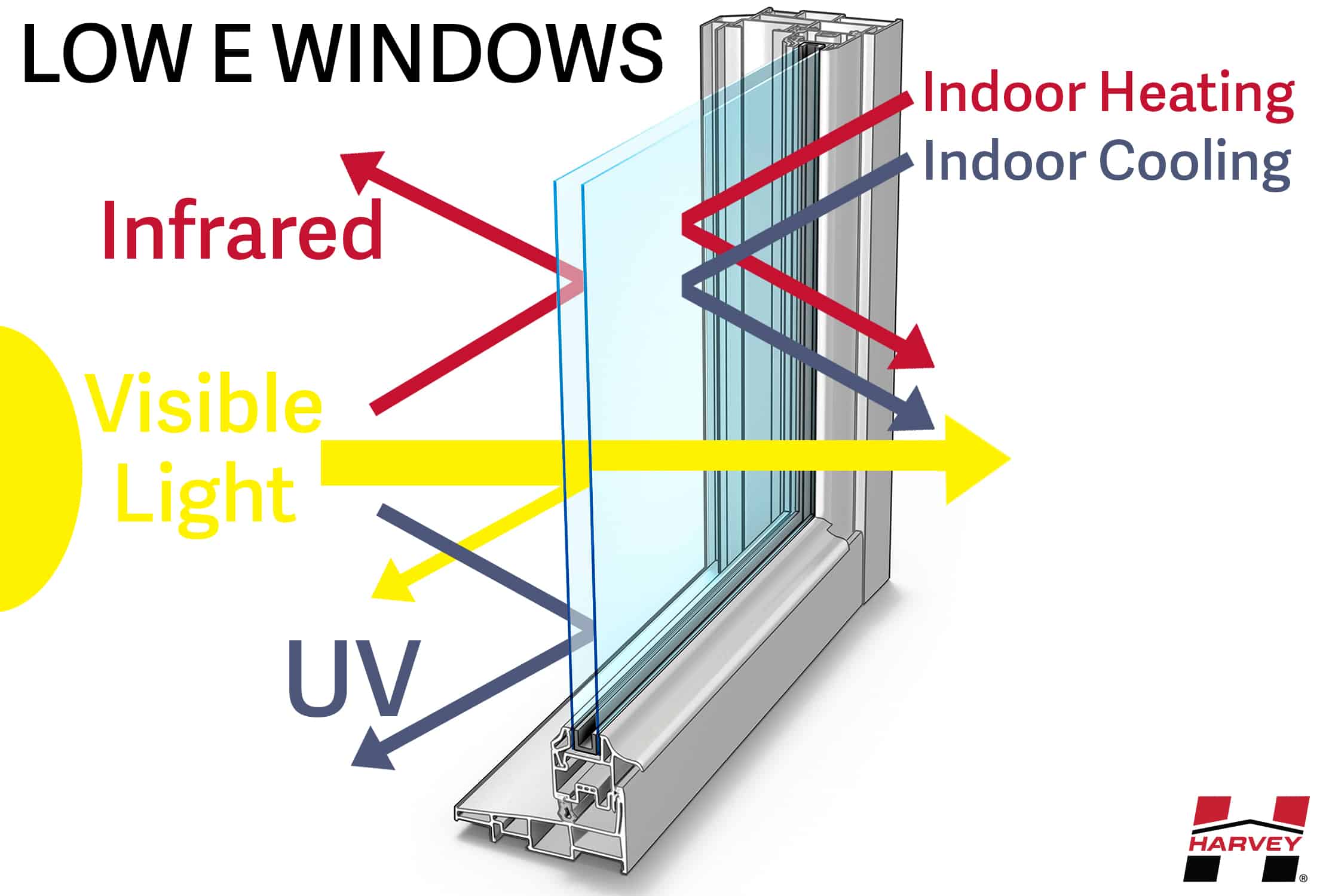
Energy Efficiency
Windows that Perform
What Makes Harvey Windows Energy Efficient?
Harvey Windows are engineered with quality materials and key features to maximize energy savings.
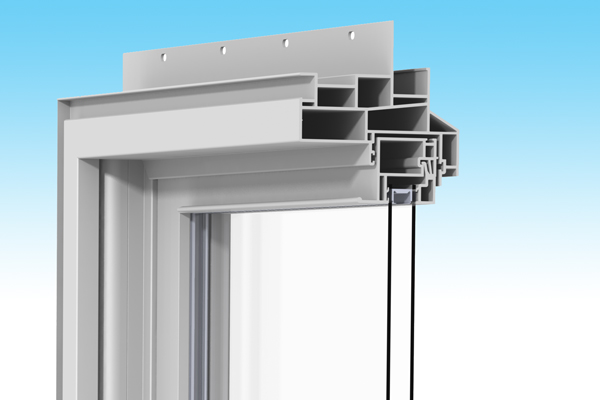
Air Infiltration Ratings
Lower quality windows lack advanced weather seals and sash-locking technology, leading to excessive air passing through the gaps where the sash meets the frame or around the perimeter of a closed window, otherwise known as a high rate of air leakage or air infiltration (AI).
Home comfort and energy consumption are greatly affected by air infiltration, so make sure you understand and consider this important rating when deciding on which window or doors to install.
The Impact on your Home
When a house has old or poor quality windows, there's a constant battle between the thermostat and the air that's leaking in, leading to wear and tear on heating/cooling systems.
In this video, see what happens to your home's comfort levels (and your wallet) when you have drafty windows.
Understanding Window Rating Values
Energy efficiency ratings shown on a product’s NFRC Label are determined by how well a window or door performs under independent testing for several criteria. Understanding how these ratings indicate a windows energy efficiency can help you make better buying decisions. Values will differ from one manufacturer to the next, and they directly impact the amount spent on heating and cooling your home.
U-Factor
Rating is a value between 0-01
U-factor (sometimes called the transfer coefficient) is a measurement of a window or door’s effectiveness as an insulator. The lower the U-factor, the longer it takes for heat to pass through it, meaning less energy is required to keep inside temperatures comfortable because it’s more insulating. Coatings, such as Low-E, are used to lower U-factor on glass, although they may impact visible transmittance.
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient
Rating is a value between 0-01
The SHGc rating is the direct measurement of how well a window or door blocks solar heat from the sun. The lower the SHGc the better the product blocks sun-generated heat. A low SHGc is essential in places like Florida, Southern California, and deeper south where this heat can vastly increase cooling costs. However, in colder climates, one might opt for a higher SHGc to utilize the suns heat. A higher SHGc can help save on heating in the colder months.
Visible Transmittance
Rating is a value between 0-01
The visible transmittance rating indicates how much light comes through a product, an important consideration when buying a window or door. VT has little to do with thermal ratings, but it does affect energy consumption. The higher this number, the better the window lets in light. A window with a high VT rating will help reduce the amount of artificial lighting needed – and therefore, energy – you consume. Before today’s window glazing techniques a brighter room was usually a hotter one but with modern window glass technology t is now possible to have a very bright room, lit only by the sun, that is just as cool as a dark room elsewhere in your home.
91583407-3c5a-48d2-ab0e-fbcd0968d831.jpg?Status=Master&sfvrsn=800bcca7_)
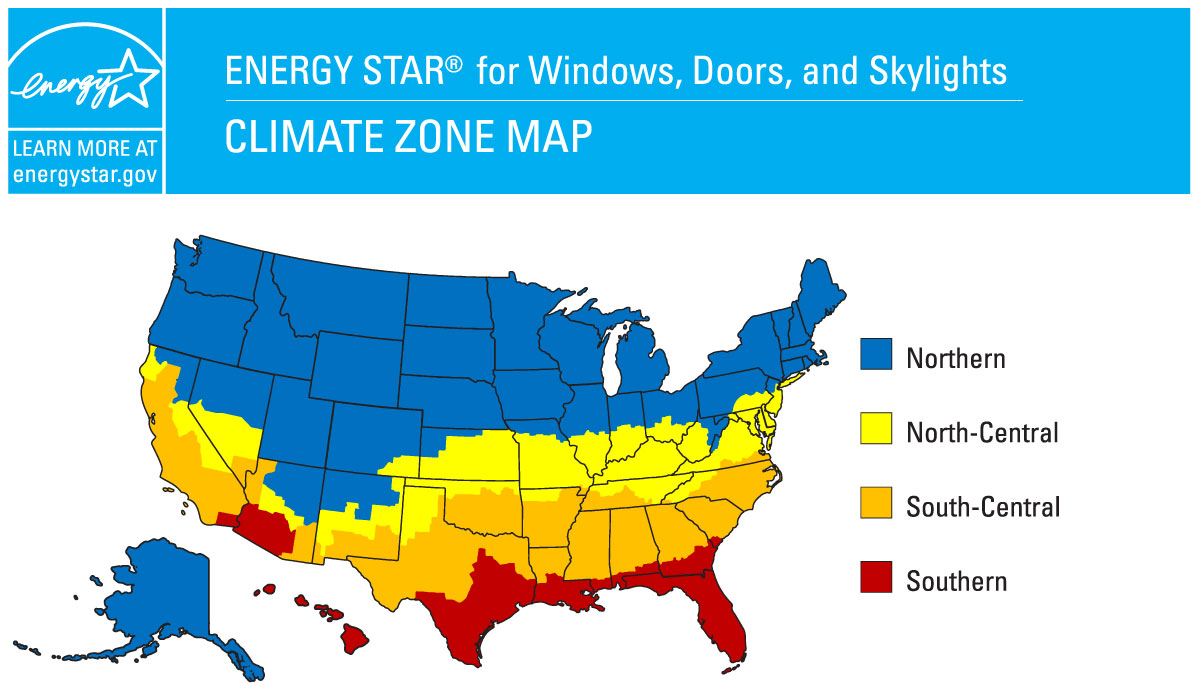
ENERGY STAR®
ENERGY STAR is a joint program of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and the U.S. Department of Energy designed to help homeowners save money and protect the environment through energy efficient products and practices. ENERGY STAR Rated products must meet minimum rating requirements for the various climate zones.
You May Also Like

3e1d3729-9515-4da4-b86b-3aa2e325b245.jpg?sfvrsn=9f0c00e3_3)
e34cdbff-0fc4-424d-8cf6-7f9c41fff88d.jpg?sfvrsn=9a81a5ce_0)