ENERGY STAR® 7.0 – What Contractors Should Know
You’re likely very familiar with the blue ENERGY STAR® label on many products that you install for customers. Do you know the process behind the program’s certification?
History Behind ENERGY STAR
The ENERGY STAR Program was established in 1992 by the EPA and the Department of Energy. Its purpose is the creation of operational and performance standards for household products which make homes and commercial buildings more energy-efficient. When companies meet these criteria, their products can be marketed with ENERGY STAR certification. From ovens that use less electricity to washing machines that do not pull excess water, ENERGY STAR has influenced nearly all manufacturing for consumer appliances.
Since its inception, ENERGY STAR partnerships have allowed American homes and businesses:
- To save 5 trillion kilowatt-hours of electricity
- To avoid more than $500 billion in energy costs
- To achieve 4 billion metric tons of greenhouse gas reductions.
In 1998, they formally added windows, doors, and skylights to their product categories, using efficiency measurements from the National Fenestration Ratings Council (NFRC). Over the following 25 years, ENERGY STAR has improved its standards for windows and doors through official iterations of its criteria. After a decade of version 6.0 as the latest requirements for certification, ENERGY STAR has enacted version 7.0.
How to Interpret 7.0 Data
As stated, ENERGY STAR uses NFRC values to gauge the energy efficiency performance of windows and doors. They focus on insulation (U-factor), solar heat gain coefficient (SHGc), and air leakage/air infiltration. U-factor refers to a door or window’s
overall insulation quality and the extent to which it can slow heat transference between the interior and exterior. The lower the U-factor, the longer it takes for heat to pass through the window, meaning less energy is required to maintain steady
indoor temperatures.
SHGC refers to a window’s capacity to provide shielding from solar heat. A low SHGc is necessary in places like Mississippi and Georgia, where year-round heat can sharply increase cooling costs. However, in colder climates, a higher SHGc number may be more desirable to encourage passive heating in the home.
Air leakage assesses the rate at which air escapes around the perimeter of a closed window. Leakage, sometimes inversely referred to as air infiltration, is measured in cubic feet per minute per square foot. The lower the infiltration rate, the less air that escapes per cubic feet per minute from the room . Windows with low air infiltration are more energy-efficient.
ENERGY STAR 7.0: Significant Changes
Version 7.0 does not reinvent the wheel, but rather draws upon years of independent, window energy performance research and testing performed after the release of 6.0. First and foremost, all ENERGY STAR window performance standards are specific to the Northern, North-Central, South-Central, and Southern climate zones of the United States. These regions experience differing temperature ranges which affects homeowners’ needs concerning windows and doors. In version 7.0, the map has been updated with more distinct zone borders. All climate zones have lower U-factors, and most have stricter SHGC numbers than before.
Updated 7.0 Window Ratings
- The rating changes shown in the graph below detail the continued effort towards standardizing better energy-efficient window and door products.
- In all regions, U-factor requirement rating numbers were lowered. Remember, the lower the U-factor number, the better the insulation.
- SHGc became stricter in Southern and South-Central regions to limit solar heat gain
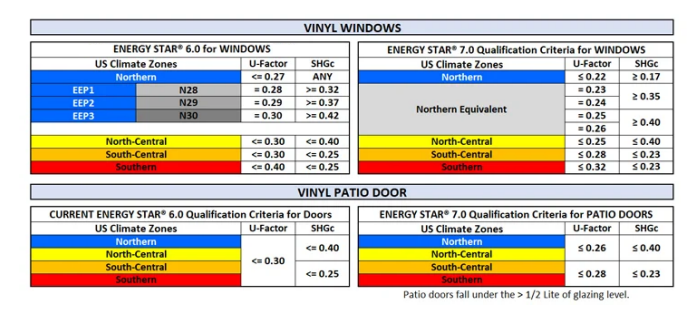
Updated 7.0 Door Ratings
- For doors with under ½ glazing, the U-factor was adjusted from a universal 0.30 to 0.26 for Northern/North Central and 0.28 for Southern/South Central.
- For doors with under ½ glazing, the SHGC went from 0.25 to 0.23 in the Southern/South Central zones, not changing in the two north regions.
Are There Incentives for Buying 7.0 Now?
The estimated energy cost savings, if 7.0 is adopted nationwide on all residential windows and doors sold, exceeds $156 billion annually, with over 53 billion pounds of yearly greenhouse gas emissions reduced. ENERGY STAR has provided information on the tax credits available for home builders who meet the energy efficient program requirements on new single-family and multifamily homes.
For homeowners, the chart below details ENERGY STAR’s projections for the annual household energy cost savings with 7.0 certified windows and doors.
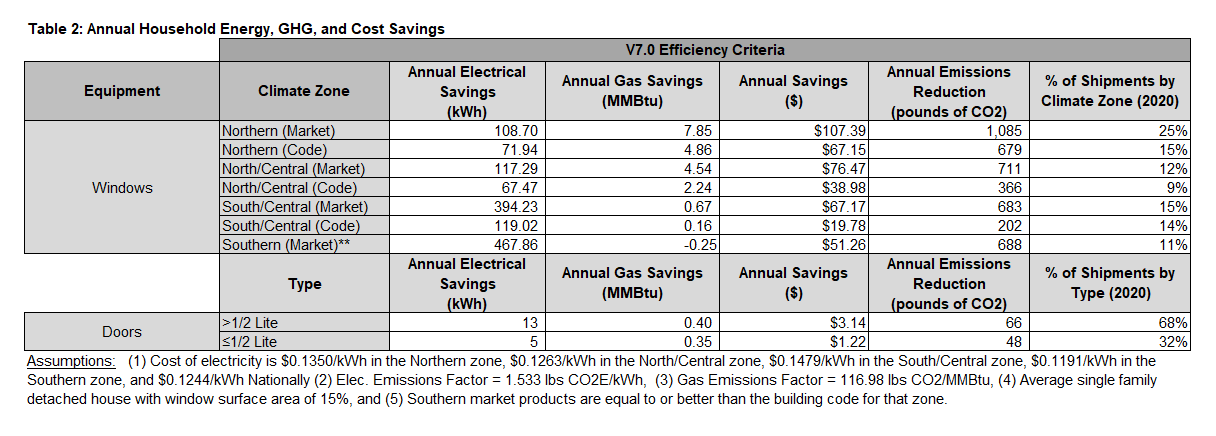
Source: ENERGY STAR® 7.0 Data Package, published October 20, 2022.
What to Tell Homeowners
After ten years, ENERGY STAR’s 6.0 standards had saturated most of the fenestration market. The 7.0 criteria will drive innovation for energy efficient design, and these changes will build upon the savings that are already attainable with the 6.0 certified products. Windows and doors that meet 7.0 criteria are a long-term investment which will make homes more comfortable in every season and reduce the cost of regular energy bills. Homeowners who choose 7.0 rated windows and doors can save thousands in energy costs over the lifetime of these products, while helping to reduce emissions.
Do remember that 6.0 windows can still provide worthwhile savings for homeowners. Depending on the scope of your home renovation project, windows certified for 6.0 may make the most sense.
Pricing Considerations
The most important aspect in quoting windows for home improvement projects or new construction is ensuring that the window’s style, design, and glass package are suitable for the homeowner's needs.
As a contractor, you can help your customers walk through the differences in performance between their choices. At Harvey, we have a range of options that can suit different climates and budgets, depending on the homeowner's goal.
Harvey’s lineup of energy-efficient glass packages provides a range of U-factors and SHGcs, allowing contractors to find the right balance between project expenses and future savings for their homeowner.
What Does Harvey have for 7.0 Products?
- Dual Low-E Coatings: Roomside for Northern (with high SHG) and North Central
- Solar Control (with or without Roomside): for South Central and Southern

Great. Where can I find Harvey 7.0 Products?
We highly recommend that you contact your regular or nearest Harvey window and door distributor in your area. If you want to learn more about how to integrate Harvey products into your business, visit our contractor page.
When ENERGY STAR was launched in 1992, Harvey Building Products was already established with 30 years of experience in manufacturing high quality windows and doors, which is how we’re able to rise to the occasion as energy-efficient criteria are updated for improved performance.
If you want to view more details of Harvey’s new glass options, view our thermal specs sheet here.
Get Insights to your Inbox |
|
Stay up-to-date with the latest trends and news. |

